SSH Key Management: Secure Your Systems & Data Today!
In an age where digital security is paramount, how do we effectively safeguard the gateways to our most sensitive systems? The answer lies in the meticulous management of Secure Shell (SSH) keys, a critical yet often overlooked facet of cybersecurity that, if mishandled, can expose organizations to significant risk.
Organizations that recognize the inherent dangers of key sprawl the uncontrolled proliferation of SSH keys across their infrastructure are increasingly adopting proactive cybersecurity measures. This typically involves deploying a dedicated SSH key management solution or an automated Privileged Password Management (PPM) system. These tools are designed to generate unique key pairs for each system, coupled with a rigorous schedule of frequent key rotation. This proactive approach is a stark contrast to the more reactive stance that characterizes many organizations, leaving them vulnerable to breaches and data compromises.
SSH keys offer a compelling alternative to traditional password-based authentication, providing a more secure and reliable method for access control. Unlike passwords, which can be susceptible to brute-force attacks, phishing, and social engineering, SSH keys rely on cryptographic principles, making them far more resistant to unauthorized access. The effectiveness of SSH keys hinges on the robustness of their management. It is this management, encompassing generation, storage, rotation, and revocation, that separates the secure from the vulnerable.
- Tom Hardy Charlotte Riley The Untold Love Story Google Discover
- Age Birthday Insights Lalisa Manoban Lisa Salvadorini Unveiled
Here's a table that summarizes the key aspects of SSH key management:
| Aspect | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Key Generation | Creating unique SSH key pairs (public and private) for each system or user. | Ensures that if one key is compromised, it doesn't expose access to all systems. |
| Key Storage | Securely storing private keys. Ideally, within a hardened system or vault. | Prevents unauthorized access to the private keys, which could be used to impersonate legitimate users. |
| Key Rotation | Regularly changing SSH keys. | Minimizes the window of opportunity for an attacker if a key is compromised. |
| Key Revocation | Disabling access via SSH keys when they are no longer needed or if compromise is suspected. | Prevents continued access by compromised keys. |
| Key Discovery | Identifying all SSH keys within an organization's infrastructure. | Provides visibility into the existing key landscape, which is critical for effective management. |
| Policy Enforcement | Implementing and enforcing policies related to SSH key usage, rotation, and access. | Ensures consistent security practices across the organization. |
- Peter Thiel The Contrarians Next Move Unveiling Insights
- Catherine Rose Young Accident Details Safety Concerns

6 SSH Key Management Best Practices
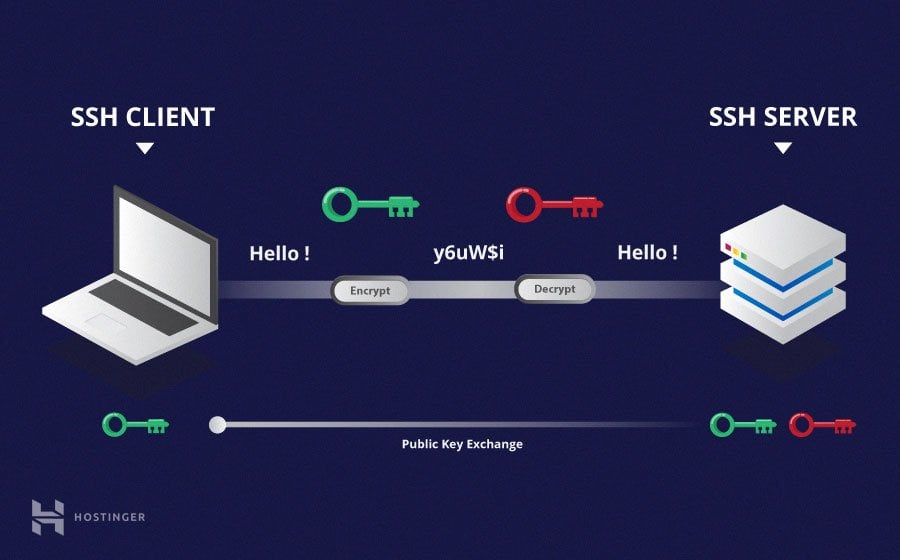
SSH Tutorial What is SSH, Encryptions and Ports
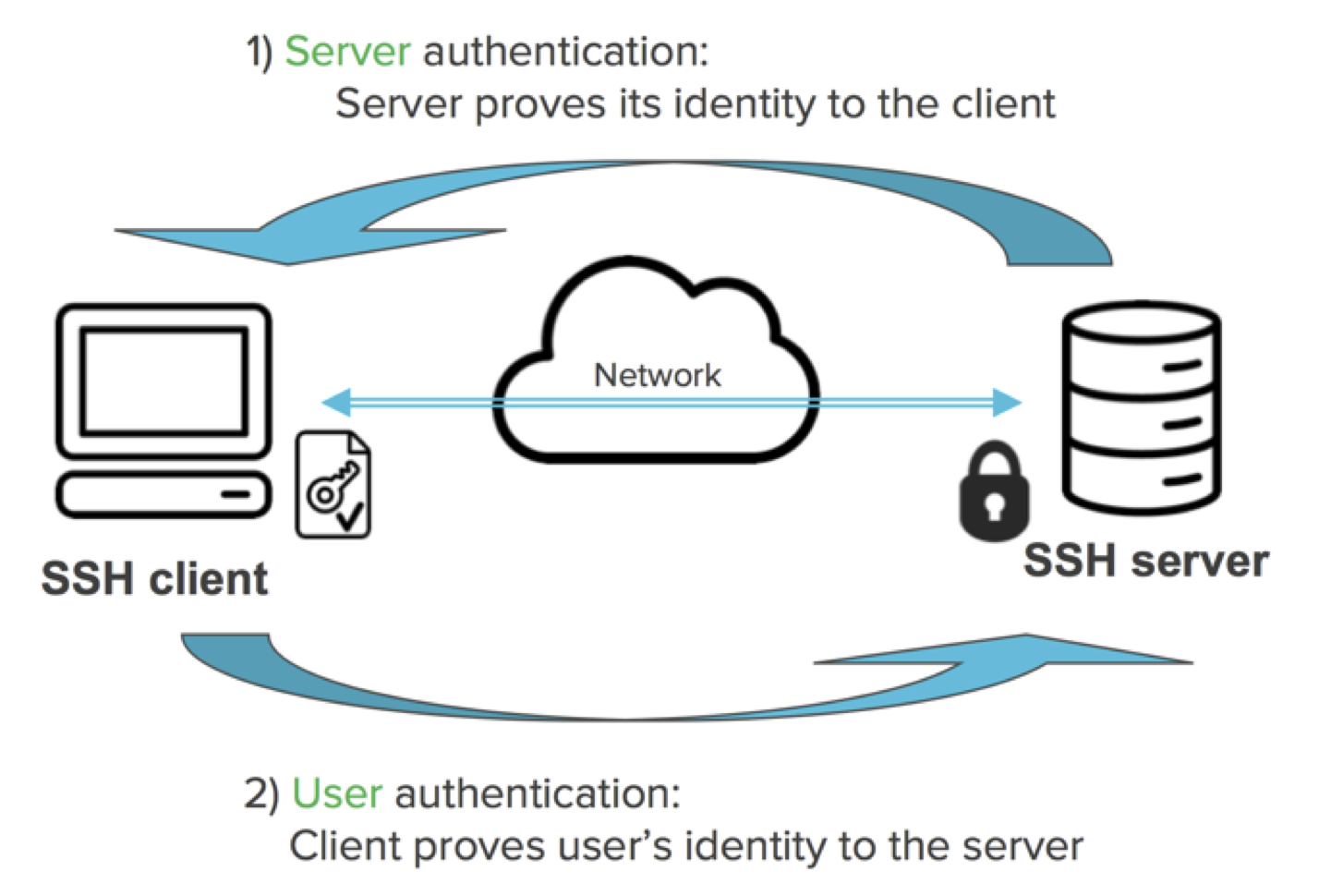
What is an SSH Key? An Overview of SSH Keys